Page 317 - TesaKatalogen
P. 317
E le c t r o n i c L e n gth M easu r i n g E q uipme n t
13
8
8
M6 M6
15 5
5 15 30 15 5 38 5 15 30
70 70
FMS 100 FMS 102
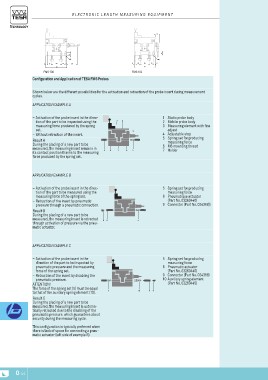
Configuration and Application of TESA FMS Probes
Shown below are the different possibilities for the activation and retraction of the probe insert during measurement
cycles.
Application example A
––Activation of the probe insert in the direc- 72 1 Static probe body
tion of the part to be inspected using the 2 Mobile probe body
measuring force produced by the spring 3 3 Measuring element with fine
set. adjust
4 Adjustable stop
––Without retraction of the insert. 5 Spring set for producing
measuring force
Result A 6 M6 mounting thread
During the placing of a new part to be 7 Holder
measured, the measuring insert remains in
its contact position thanks to the measuring 4 6 1 65
force produced by the spring set.
Application example B
––Activation of the probe insert in the direc- 98 5 Spring set for producing
tion of the part to be measured using the measuring force
measuring force of the spring set. 8 Pneumatique actuator
(Part No. 03260440)
––Retraction of the insert by pneumatic 9 Connector (Part No. 024388))
pressure through a pneumatic connection.
5
Result B
During the placing of a new part to be
measured, the measuring insert is retracted
through activation of pressure via the pneu-
matic actuator.
Application example C
––Activation of the probe insert in the 5 5 Spring set for producing
direction of the part to be inspected by measuring force
pneumatic pressure and the measuring 8 Pneumatic actuator
force of the spring set. (Part No. 03260440)
9 Connector (Part No. 024388)
––Retraction of the insert by disabling the 10 Auxiliary spring element
pneumatic pressure. (Part No. 03260445)
ATTENTION ! 10 8 9
The force of the spring set (5) must be equal
to that of the auxiliary spring element (10).
Result C
During the placing of a new part to be
measured, the measuring insert is automa-
tically retracted due to the disabling of the
pneumatic pressure. which guarantees about
security during the measuring cycle.
This configuration is typically preferred when
there is lack of space for connecting a pneu-
matic actuator (left side of example B).
O-44