Page 7 - TesaKatalogen
P. 7
What is known...
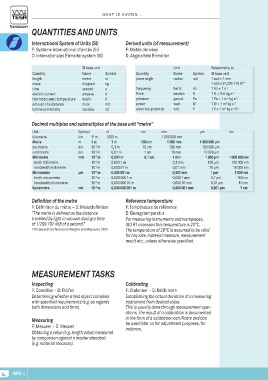
Quantities and Units Derived units (of measurement)
F: Unités dérivées
International System of Units (SI)
F: Système international d’unités (SI) D: Abgeleitete Einheiten
D: Internationales Einheitensystem (SI)
Quantity SI base unit Symbol Quantity Unit Symbol Relationship to
length m plane angle Name rad
mass Name kg radian SI base unit
time metre s frequency Hz 1 rad = 1 mm
electric current kilogram A force hertz N 1 rad = 57,295 779 51°
thermodynamic temperature second K pressure newton Pa 1 Hz = 1 s-1
amount of substance ampere md power pascal W 1 N = 1 m kg s-2
luminous intensity kelvin cd electrical potential watt V 1 Pa = 1 m-1 kg s-2
mole volt 1 W = 1 m2 kg s-3
candela 1 V = 1 m2 kg s-3 A-1
Decimal multiples and submultiples of the base unit "metre"
Unit Symbol m cm mm µm nm
kilometre km 13 m 1000 m 100 cm 1 000 000 mm 1 000 000 µm 1 000 000 nm
Metre m 1m 1 m 10 cm 1 000 mm 100 000 µm 100 000 nm
decimetre dm 10-1 m 0,1 m 1 cm 100 mm 10 000 µm 10 000 nm
0,1 cm 1 000 µm 1 000 nm
centimetre cm 10-2 m 0,01 m 10 mm 100 µm 100 nm
Millimetre mm 10-3 m 0,001 m 1 mm 10 µm 10 nm
tenth millimetre 0,000 1 m 0,1 mm 1 µm 1 nm
10-4 m 0,1 µm
hundredth millimetre 0,000 01 m 0,01 mm 0,01 µm
Micrometre 10-5 m 0,000 001 m 0,001 mm 0,001 µm
tenth micrometre µm 10-6 m 0,000 000 1 m 0,000 1 mm
hundredth micrometre 10-7 m 0,000 000 01 m 0,000 01 mm
Nanometre 0,000 000 001 m 0,000 001 mm
10-8 m
nm 10-9 m
Definition of the metre Reference temperature
F: Définition du mètre – D: Meterdefinition F: Température de référence
"The metre is defined as the distance
travelled by light in vacuum during a time D: Bezugstemperatur
of 1/299 792 458 of a second." For measuring instruments and workpieces,
ISO R1 assesses this temperature is 20°C.
17th General Conference on Weights and Measures, 1983. The temperature of 20°C is assumed to be valid
for any size, material measure, measurement
result etc., unless otherwise specified.
Measurement tasks Calibrating
F: Etalonner – D: Kalibrieren
Inspecting
F: Contrôler – D: Prüfen Establishing the actual deviation of a measuring
Determining whether a test object complies instrument from desired value.
with specified requirements (e.g. as regards This is usually done through measurement oper
both dimensions and form). ations. The result of a calibration is documented
in the form of a calibration certificate and can
Measuring be used later on for adjustment purposes, for
F: Mesurer – D: Messen instance.
Obtaining a value (e.g. length value) measured
by comparison against a master s tandard
(e.g. material measure).
INFO-6